Radar
Links to things we’re checking into.
Get This and Other Things In Our Weekly Email Newsletter
Geist
Geist embodies our design principles of simplicity, minimalism, and speed, drawing inspiration from the renowned Swiss design movement. With precision, clarity, and functionality at its core, Geist enhances the visual experience of developers...
Relative Colors
Over the years, we have been used to using CSS pre-processors like Sass for a use case like applying opacity to a pre-defined color. Today, we have a new way to do that and more with CSS relative colors. In this article, I aim to shed the light on that and introduce...
Screenity
A screen recorder that's free, private, and friendly With Screenity you can relax. No time limits, an easy interface, and awesome features.
Omatsuri
Open source browser tools for everyday use
SVG Repo
500.000+ Open-licensed SVG Vector and Icons Search, explore and edit the best-fitting free icons or vectors for your projects using a wide variety vector library. Download free SVG vectors and icons for commercial use.
Quick Reference
Here are some cheatsheets and quick references contributed by open source angels.
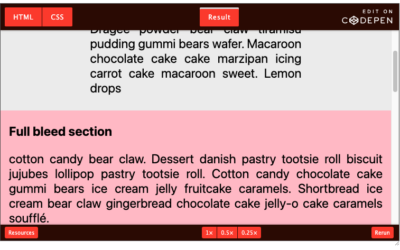
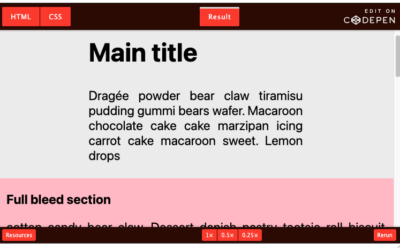
Full-Bleed Layout with Modern CSS
Cool, right? Not only have we created a full-bleed layout with compact code but we can easily adjust it to control the margin behavior of the elements. Can you think of other variations? I am sure we could tweak the formulas to have other useful and interesting...
Should navigation bars be sticky or fixed?
Like most UX design decisions, choosing the best type of navigation isn’t a one-size-fits-all verdict. It depends on your digital product, target users, and UX goals.
VIET GD
A casual index, archive, and celebration of Vietnamese graphic design. Currently, there are 274 objects in this collection.
How To Use Chrome’s Developer Tools
This article provides an introduction to Chrome DevTools and then takes a look at some more advanced features.
tinygradient
Easily generate color gradients with an unlimited number of color stops and steps.
State of React 2024
Instead, React 19 focused on taking a lot of our pain away, from making forwardRef obsolete, to diffs for hydration errors, to a new compiler that makes our code more performant with minimal extra work on our part.
Flexbox bulider
Build 'em yay
Chuck Norris red
Setting the colour of text on a webpage is usually a simple affair involving whipping it out the good ol' CSS color property. But this is HTMHell, dammit. None of that wishy-washy CSS nonsense here. No siree. We use HTML as the good lord intended and shalln't stray...
Hero Patterns
A collection of repeatable SVG background patterns for you to use on your web projects.
postspark.app
Take slick screenshots and product image grabs.
Every HTML element
There are over a hundred HTML elements. This page uses all of them. You're looking at <p></p> right now.
Optimizing Images for Web Performance
Images make websites look great, but they’re also the biggest performance bottleneck. They add huge file sizes, delay Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), and can even mess with Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) if they aren’t handled properly. And while developers are quick...
How to Retain Customers, When AI is Pushing Them to Competitors
You don’t just lose customers to price—you lose them to hesitation.
Build for the Web, Build on the Web, Build with the Web
If you’re going to go all-in on a framework or, heaven forbid, an SPA, give the long term some serious consideration, and make sure you do a really, really good job.
litur
A color picker for the real world. Find, collect and organize all the colors around you.A designer’s best-kept secret, a developer's best friend.
Understanding Accessibility.
Accessibility should be at the core of web design. Colour, typography, animations and images need to be applied according to certain rules so that information can be digested easily. Designers need to understand how people with (and without) disabilities...
untools
Thinking tools and frameworks to help you solve problems, make decisions and understand systems.
Figcomponents.com
We've curated the best Figma components in one place. Discover, copy and paste UI components in Figma with the most efficient way to build designs. Get all the essentials for any design project in one place. From buttons to data visualizations, you'll find the perfect...
Logoipsum
117 free placeholder logos
Landing Pages Explained
The only collection of leading SaaS and creator landing pages with expert explanations of the ideas used to increase conversion
Website hero section library
Curated collection of beautiful website hero sections.
Extending the cursor
The cursor has transformed from a simple pointing device into a powerful tool for enhancing user interaction and providing contextual feedback. Software and games are raising the bar for what the cursor interface can do, demonstrating how thoughtful extensions of a...
Full-Bleed Layout with Modern CSS
I recently shared a trick on how to create a Full-bleed layout using a few lines of modern CSS code. If you are unfamiliar with such layout see the demo below. In this article we’ll dig deeper into the idea and explain things as we go.
Dark Mode and Accessibility: Finding the Right Balance
It didn’t take long for the “dark mode” to become a requirement for every user interface design. What started out as a design trend turned into a must-have feature for offering a comfortable user experience.
Should navigation bars be sticky or fixed?
Like most UX design decisions, choosing the best type of navigation isn’t a one-size-fits-all verdict. It depends on your digital product, target users, and UX goals.
Learn Shader Programming with Rick and Morty
This animation of Rick was made with 240 lines of code. No libraries, no images. I’m going to show you how to use GPU shaders and signed distance fields to make animations like it for videos, video games, or just for fun! I even built a live coding editor into the...
CSS text-box-trim
Take back space from above and below your text content; achieve optical balance.
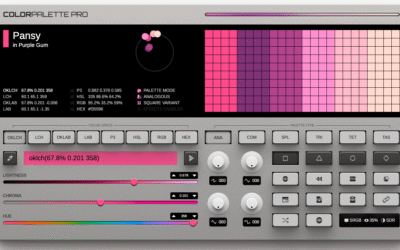
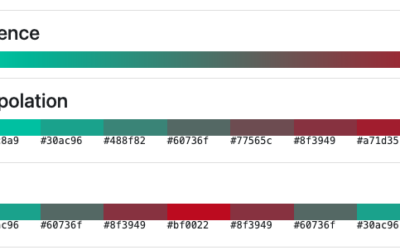
Super Color Palette
Generate super awesome color palettes by shifting hue, saturation, lightness, and more!
Thoughts on Tailwind 4
The Tailwind CSS v4.0 beta was just released, and I wanted to share some thoughts on it. More specifically, I have some concerns that I have not seen covered elsewhere.
Design for Real Life – Eric Meyer and Sara Wachter-Boettcher
Join Sara Wachter-Boettcher and Eric Meyer as they turn examples from more than a dozen sites and services into a set of principles you can apply right now. Whether you're a designer, developer, content strategist, or anyone who creates user experiences, you'll gain...
More News & Articles
How to use Font Awesome, The Easy Way
Really quick tutorial and code snippets on using Font Awesome on a web page.
Stop Letting Your Inbox Control You – Strategies for Managing Work Emails
Constantly responding to emails drains productivity and fuels burnout. Set boundaries, manage expectations, and reclaim focus with intentional email habits. Prioritize deep work over urgency and take control of your inbox.
Website Scanning Patterns for Maximum Engagement
Discover how users visually process websites, the role of scanning patterns, content placement, and “the fold” Learn to design engaging pages with fast-to-consume content that aligns with user behavior.